When it comes to powering homes and businesses, electricity consumption is a significant factor. While most residential properties utilize single-phase power, industrial facilities often rely on 3-phase power. This article delves into the key differences between 3-phase and single-phase power consumption, exploring their applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
Single-Phase Power Consumption: An Overview
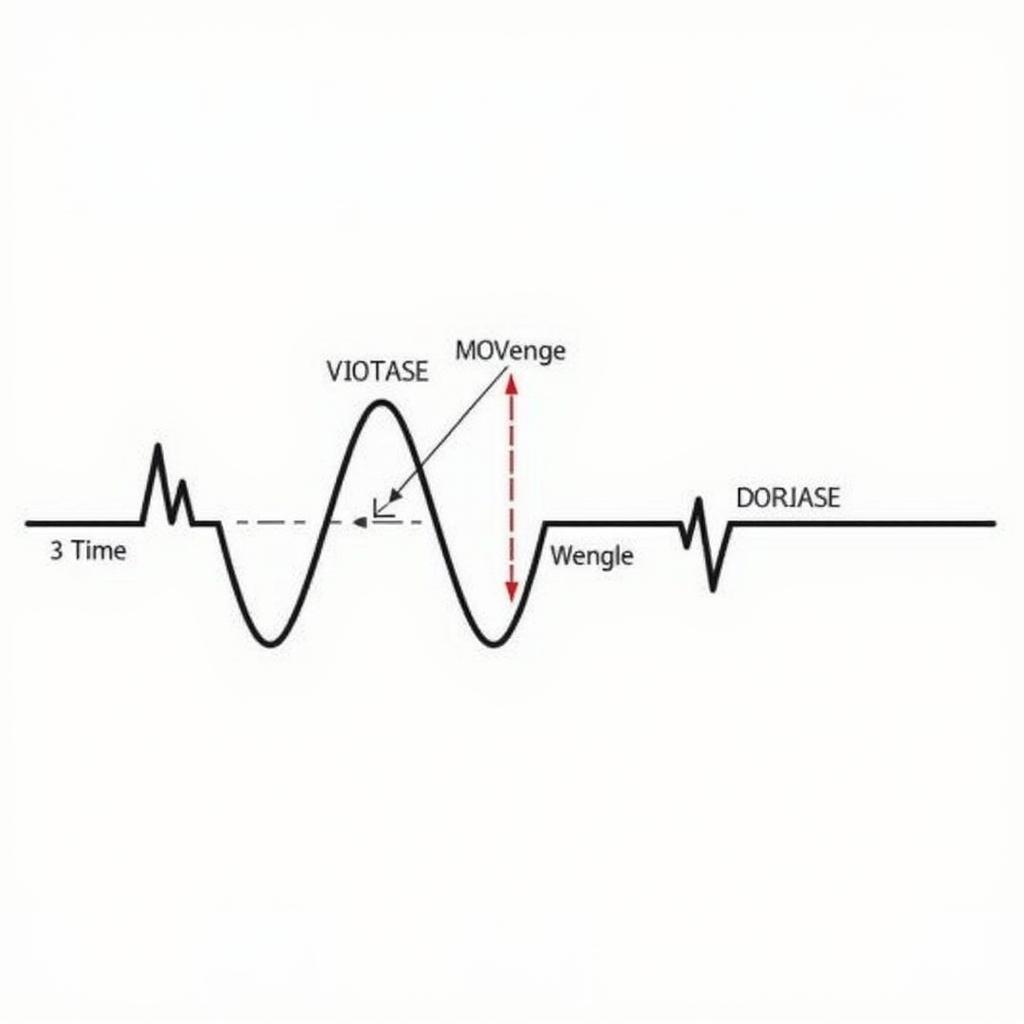 Single-Phase Power Illustration
Single-Phase Power Illustration
Single-phase power, as its name suggests, utilizes a single alternating current (AC) waveform to deliver electricity. Imagine a single sine wave representing the flow of electricity. This wave oscillates between positive and negative values, completing a full cycle several times per second. In most countries, the standard frequency for single-phase power is either 50Hz or 60Hz.
Homes typically use single-phase power for running everyday appliances. From refrigerators and washing machines to lighting fixtures and electronic devices, single-phase power efficiently handles the electrical demands of most residential settings. This power system is cost-effective for distributing electricity over shorter distances, making it ideal for residential areas.
Understanding 3-Phase Power Consumption
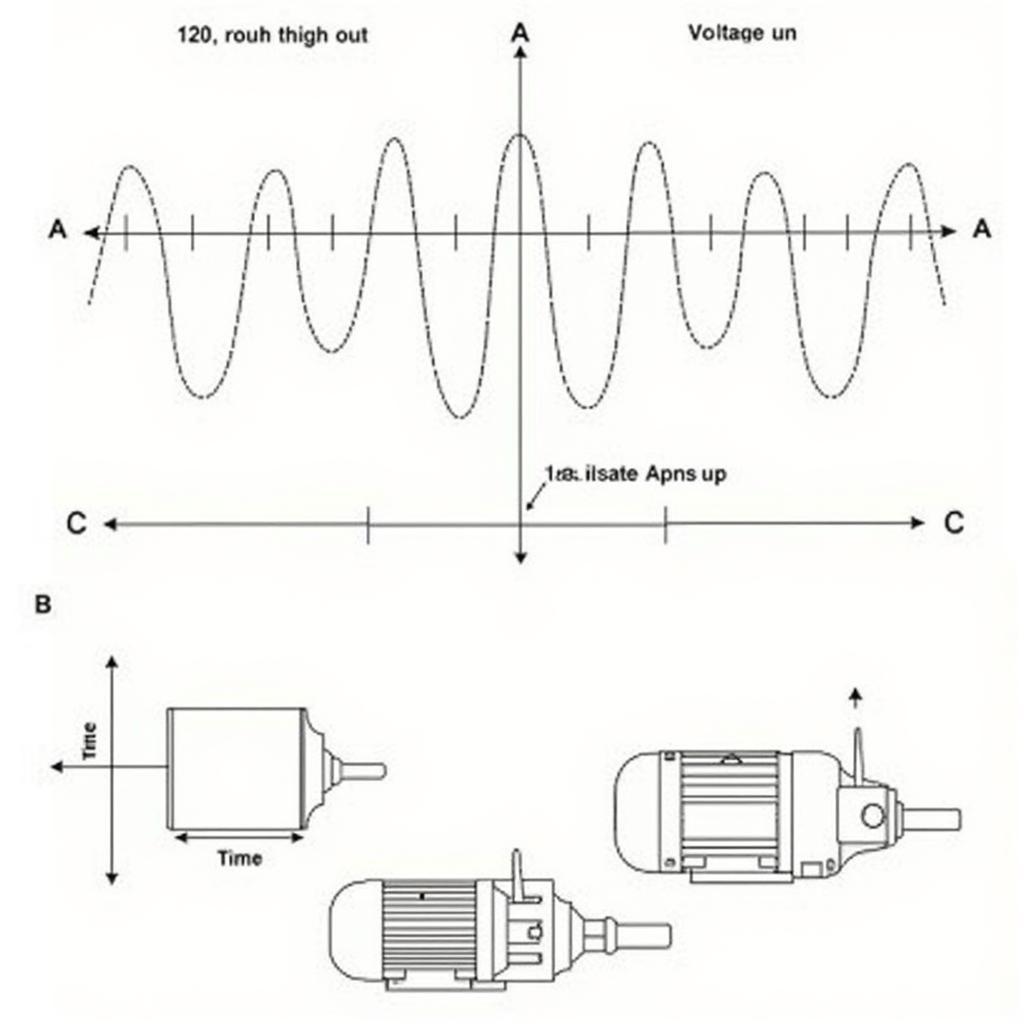 Three-Phase Power System
Three-Phase Power System
In contrast to single-phase power, 3-phase power utilizes three separate conductors, each carrying an alternating current waveform. However, these waveforms are not in sync but rather offset by 120 degrees. This phase difference results in a continuous flow of power, unlike the pulsating power delivery of single-phase systems.
This constant power delivery makes 3-phase power systems highly efficient for high-power applications. Industries rely heavily on 3-phase power to operate heavy machinery, large motors, and other equipment that demand significant electrical power. The efficiency of 3-phase power also translates into reduced power loss during transmission, making it a cost-effective choice for industrial settings.
Comparing 3-Phase and Single-Phase Power Consumption: Key Differences
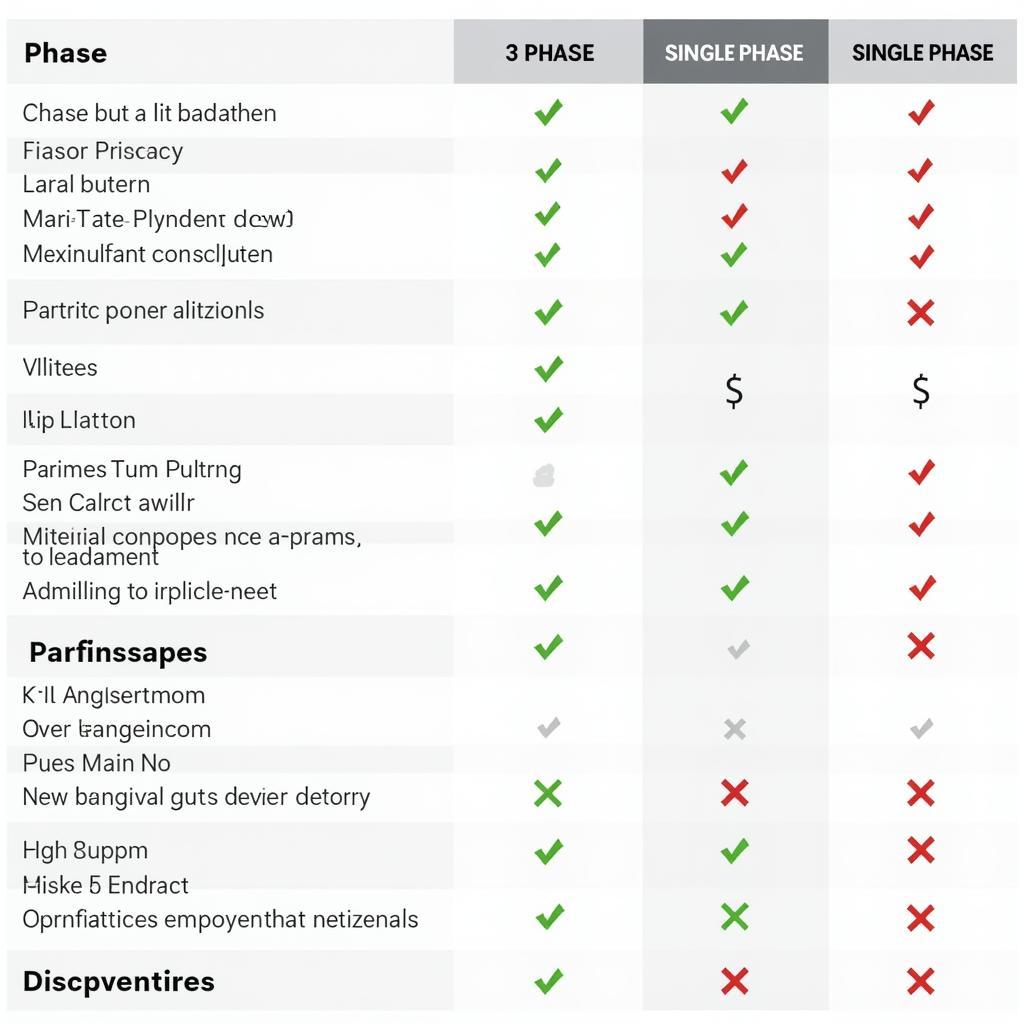 Comparison Table: 3-Phase vs. Single-Phase Power
Comparison Table: 3-Phase vs. Single-Phase Power
While both 3-phase and single-phase power systems serve the purpose of delivering electricity, their applications, advantages, and disadvantages differ significantly:
Voltage: Single-phase systems typically operate at lower voltages, commonly 120V or 240V. In contrast, 3-phase systems utilize higher voltages, ranging from 208V to 480V, depending on the application and regional standards.
Phases: As their names suggest, single-phase power uses one phase, while 3-phase power employs three phases offset by 120 degrees. This phase difference is crucial in providing a constant and efficient power supply.
Applications: Single-phase power is suitable for most residential applications, powering common household appliances and electronics. On the other hand, 3-phase power is essential for industrial applications, running heavy machinery, large motors, and other high-power equipment.
Advantages: Single-phase systems are cost-effective for residential use, with simpler wiring and lower installation costs. Three-phase systems offer greater power efficiency, reduced power loss, and the ability to handle higher loads, making them ideal for industrial settings.
Disadvantages: Single-phase systems have limitations in power output and are not suitable for heavy-duty applications. Three-phase systems, while more efficient, come with higher installation costs and more complex wiring requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between 3-phase and single-phase power consumption is crucial when deciding on the appropriate electrical system for a particular application. While single-phase power remains the standard for residential use, 3-phase power is indispensable for industrial operations demanding high power and efficiency.
Need help with your power consumption needs?
Contact us at:
Phone: 0372999888
Email: aibongda@gmail.com
Address: 236 Cầu Giấy, Hà Nội
Our 24/7 customer support team is here to assist you!