Calvinism and Arminianism represent two prominent theological systems within Protestant Christianity. These two schools of thought offer differing perspectives on the nature of salvation and God’s sovereignty. Understanding the core distinctions between Calvinism and Arminianism is crucial for navigating the complexities of Christian theology.
What is Calvinism?
Calvinism, based on the teachings of John Calvin, emphasizes God’s sovereignty and predestination. It posits that God has pre-ordained everything that will happen, including who will be saved.
- Total Depravity: Humans are inherently sinful and unable to choose God on their own.
- Unconditional Election: God chooses to save some individuals based solely on His will, not on any human merit.
- Limited Atonement: Christ’s death atoned for the sins of the elect only, not for everyone.
- Irresistible Grace: Those whom God has chosen will inevitably be saved; they cannot resist God’s grace.
- Perseverance of the Saints: Those who are truly saved will persevere in their faith until the end.
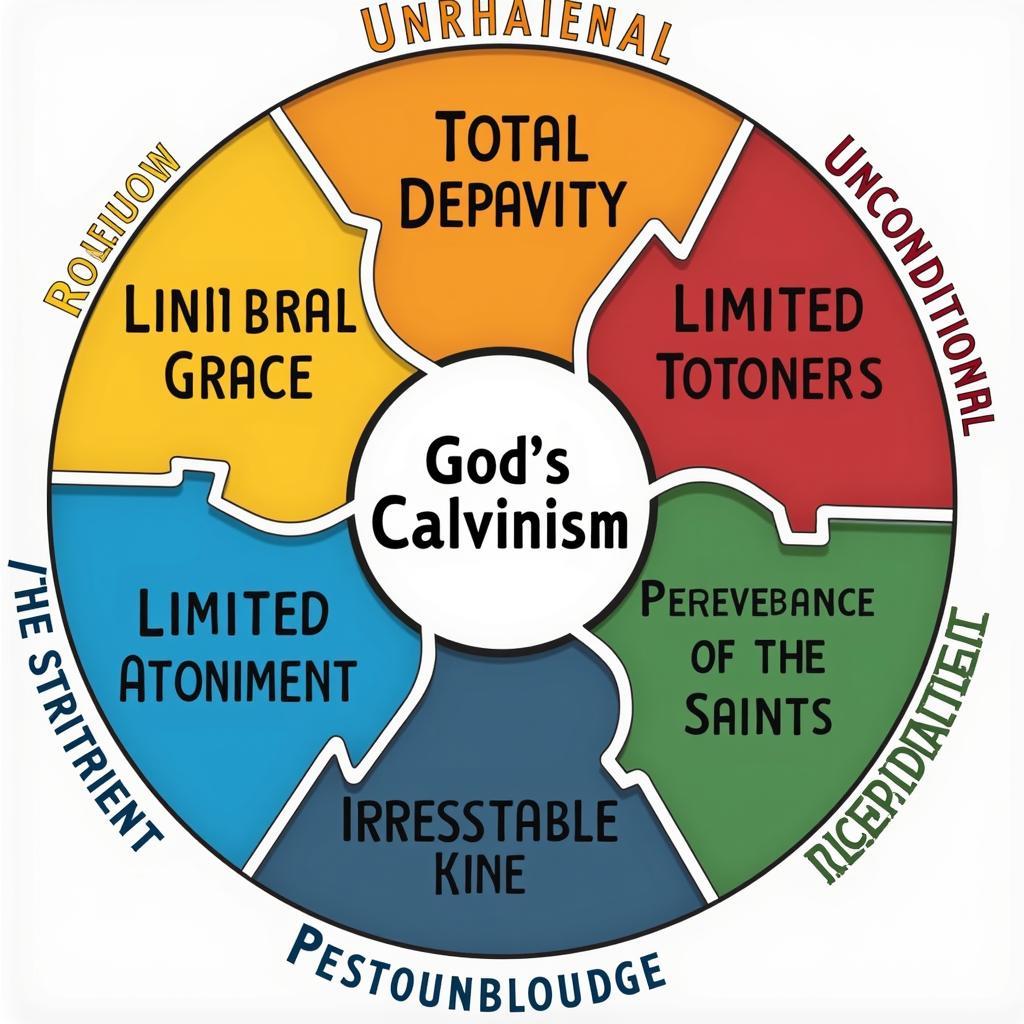 Calvinism's Five Points
Calvinism's Five Points
This system emphasizes God’s absolute control and the assurance of salvation for the elect.
What is Arminianism?
Arminianism, named after Jacobus Arminius, emphasizes human free will and God’s universal love. It argues that God desires all people to be saved and provides the opportunity for everyone to choose.
- Free Will: Humans have the ability to choose or reject God’s grace.
- Conditional Election: God’s election is based on His foreknowledge of who will freely choose to believe in Christ.
- Unlimited Atonement: Christ’s death atoned for the sins of all people.
- Prevenient Grace: God’s grace enables everyone to respond to the Gospel. This grace can be resisted.
- Conditional Security: Salvation can be lost if a believer persistently rejects God’s grace and turns away from faith. (Note: some Arminians hold to Eternal Security, the belief that salvation cannot be lost).
 Key Principles of Arminianism
Key Principles of Arminianism
Arminianism highlights the importance of human response in salvation and God’s desire for all people to come to Him.
Calvinism vs Arminianism: Key Differences Explained
The core difference between Calvinism and Arminianism centers on the interplay between God’s sovereignty and human free will. Calvinism emphasizes God’s absolute control, while Arminianism emphasizes human agency in choosing salvation.
Predestination vs. Free Will: Who is in Control?
Calvinists believe God predestines individuals for salvation, while Arminians believe humans freely choose to accept or reject God’s grace.
The Extent of the Atonement: Who did Christ Die For?
Calvinists believe Christ’s atonement was limited to the elect, while Arminians believe it was available to all people.
The Nature of Grace: Can it be Resisted?
Calvinists believe God’s grace is irresistible, while Arminians believe it can be resisted.
“The key is to understand that both Calvinism and Arminianism are attempting to grapple with the vastness of God’s nature and His relationship with humanity,” says Dr. Emily Carter, Professor of Theology at Divinity Seminary. “Both systems offer valuable insights into the nature of God and salvation.”
Conclusion
Calvinism and Arminianism are complex theological systems that offer differing perspectives on God’s sovereignty and human responsibility in salvation. While these two systems have key differences, both attempt to understand the profound nature of God’s relationship with humanity. Understanding these differences is crucial for navigating the complexities of Christian theology.
FAQ
-
What are the five points of Calvinism?
Total Depravity, Unconditional Election, Limited Atonement, Irresistible Grace, and Perseverance of the Saints. -
What are the key tenets of Arminianism?
Free Will, Conditional Election, Unlimited Atonement, Prevenient Grace, and Conditional Security (or Eternal Security). -
What is the main difference between Calvinism and Arminianism?
The primary difference lies in their understanding of God’s sovereignty and human free will. -
Can someone be a Christian and not subscribe to either Calvinism or Arminianism?
Yes, many Christians hold beliefs that don’t perfectly align with either system. -
Are there other theological systems besides Calvinism and Arminianism?
Yes, there are numerous other theological viewpoints within Christianity. -
Which system is correct?
Both systems have valid interpretations of scripture, and the “correct” system is a matter of theological debate. -
How can I learn more about Calvinism and Arminianism?
Further research and study of theological resources can provide a deeper understanding.
Khi cần hỗ trợ hãy liên hệ Số Điện Thoại: 0372999888, Email: [email protected] Hoặc đến địa chỉ: 236 Cầu Giấy, Hà Nội. Chúng tôi có đội ngũ chăm sóc khách hàng 24/7.